| Fixed star: AVIOR | |
| Constellation: Epsilon (ε) Carina in Argo Navis | |
| Longitude 1900: 21VIR47 | Longitude 2000: 23VIR08 |
| Declination 1900: -59.11′ | Declination 2000: -59.31′ |
| Right ascension: 08h 22m | Latitude: -72.40′ |
| Spectral class: KB | Magnitude: 1.7 |
The history of the star: Avior
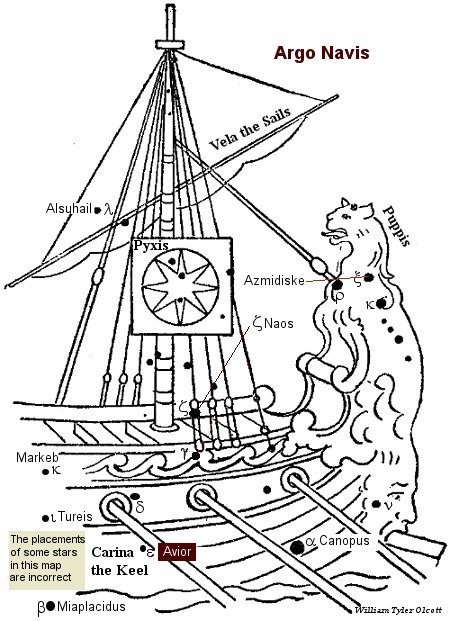
Epsilon (ε) Carina, Avior, is a southern star in the Keel of the Great Ship.
Wikipedia explains that this star, epsilon Carina, is also known by the name Avior, but this is not a classical name. It was assigned to the star by Her Majesty’s Nautical Almanac Office in the late 1930s during the creation of The Air Almanac, a navigational almanac for the Royal Air Force.
The astrological influences of the constellation Carina
No myths or astrological interpretations are associated with the constellation Carina because this constellation had always been seen as part of the constellation Argo Navis, the Great Ship, until French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1752 subdivided Argo Navis into Carina (the keel of the ship), Puppis (the poop), and Vela (the sails), plus a subordinate division of Argo now called Pyxis Nautica. The constellation Argo Navis represents the ship in which Jason brought the Golden Fleece from Colchis, said to be the first ship ever built.
The astrological influences for the whole constellation of Argo Navis, the Great Ship: According to Ptolemy the bright stars are like Saturn and Jupiter. Argo is said to give prosperity in trade and voyages, and strength of mind and spirit, but it has been observed to accompany cases of drowning, a notable instance being furnished by the horoscope of Shelley, where Argo occupied the 8th house and contained the Sun, Venus and Uranus. Drowning is particularly to be feared when Saturn afflicts the Moon in or from Argo. It is probably on account of this constellation that Virgo, especially the first decanate, is frequently found to be connected with drowning. [Robson, p.30.]